Osteochondrosis is a process of degeneration, aging, degradation of cartilage tissue and its transformation into a kind of bone.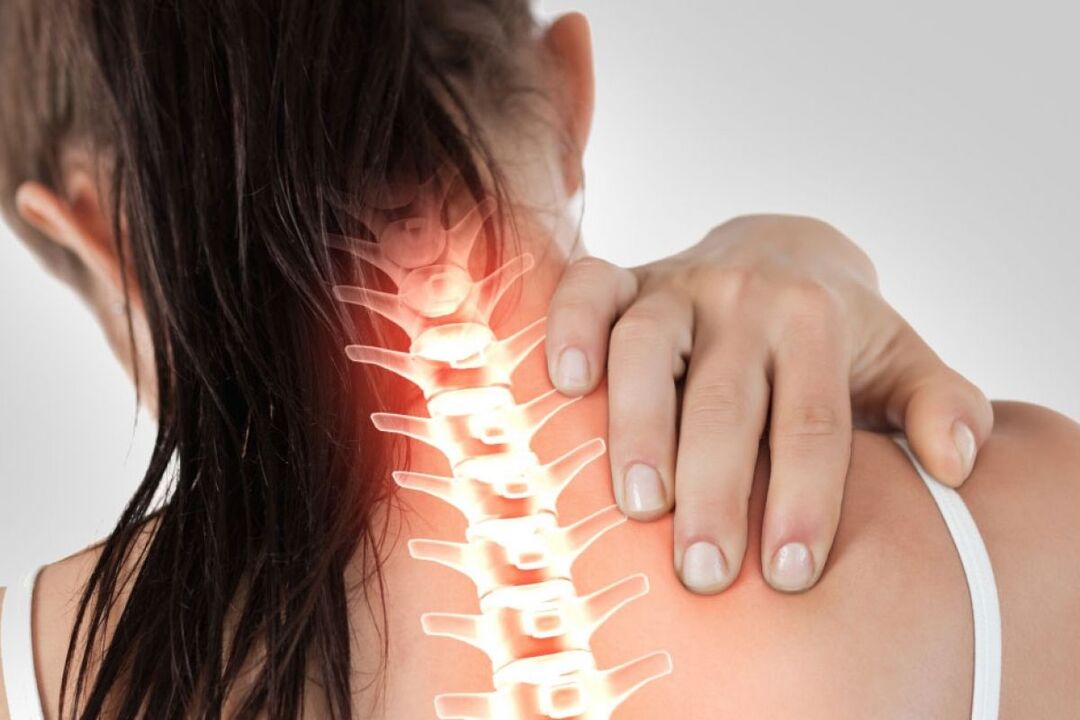 To understand the problem of osteochondrosis, it is necessary to imagine the structure of the spine: it consists of 35 vertebrae, which are placed one above the other in one column, forming a vertebral column. Between the vertebrae there are "pads" - cartilaginous discs (they act as shock absorbers and lubricants when the vertebrae move), the discs consist of a multilayered rigid ring and a liquid gelatinous core in the center.
To understand the problem of osteochondrosis, it is necessary to imagine the structure of the spine: it consists of 35 vertebrae, which are placed one above the other in one column, forming a vertebral column. Between the vertebrae there are "pads" - cartilaginous discs (they act as shock absorbers and lubricants when the vertebrae move), the discs consist of a multilayered rigid ring and a liquid gelatinous core in the center.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis:
Everyone knows that the spine becomes thinner in the structure closest to the head. The upper vertebrae that make up the cervical region are long, refined, but very strong and mobile. However, their strength is not unlimited, especially when the daily stress on the neck exceeds the norm. The main causes of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are always hidden in these loads.
How osteochondrosis of the cervical spine manifests itself also depends on the type of load and the place of damage to the vertebral discs: each nerve root is responsible for a particular function, so the manifestations of osteochondrosis of the neck are so diverse. The development of the disease occurs in 4 stages. Each subsequent is more difficult than the previous one.
Stage 1 cervical osteochondrosis:
How can our spine protect itself from overuse and destructive physical activity (or inactivity)?
First of all, discomfort: stretching, tingling, pulling - all these are the first signs of any disease of the spine.
Intervertebral osteochondrosis of the cervical spine begins with a feeling of tension in the neck muscles, their fatigue. The patient may feel a slight pain, creak when turning and tilt the head. Quite often, this discomfort is perceived as "probably cold" or "I'm tired of something".
Remember! Pain is a sign, we can say the signaling of our body, if it worked it's not just that. Pain cannot be ignored or numbed with pills!
Phase 2:
The patient already feels more intense pain when he turns and tilts his head. Sometimes the pain radiates (spreads) to the right or left arm, to the shoulder joint, sometimes to the hand.
On the part of the nervous system, there are still rare headaches, fatigue, fatigue, a state of distraction (the initial symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women are very similar to the cyclic symptoms of the reproductive system: headache, dizziness, feeling of weakness, fatigue).
Even if the signs of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine have already become evident, in the second stage there are still all possibilities to prevent the development of the disease and the appearance of complications. It is especially important to prevent the development of hernias, which in the cervical spine can be dangerous with loss of mobility and impaired blood supply to the brain.
Phase 3:
At the third stage, the disease can already be considered neglected, because the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine at this stage is already much more difficult, and the destruction is often irreversible. The pain increases as intervertebral hernias begin to appear.
Constant weakness and dizziness - due to pinching of the nerves and large vessels that feed the cerebral cortex, are also intensified. Pain is often given to the hands. The innervation of the muscles of the upper extremities is disturbed, as a result of which they weaken. Numbness and tingling in the hands are a common symptom of third-degree degenerative disc disease in the neck.
Step 4:
The intervertebral discs have already been significantly destroyed and have undergone major changes, hernias and protrusions of each of them have a significant impact on the patient's well-being. In place of the destroyed discs, connective tissue appears, which deprives the spine of flexibility.
Compression of the nerves and blood vessels leads to impaired coordination. Pain, sleepiness, lethargy, and dizziness are worse. To these are added the ringing in the ears. There is a huge risk of diseases that can be caused by osteochondrosis:
- When a vertebral artery is compressed by a hernia, it leads to cerebral ischemia and develops into a spinal stroke;
- Pinching of blood vessels can lead to malnutrition in the cortex or lower parts of the brain. As a result: impaired perception, loss of consciousness;
- Spinal cord compression can also be fatal.